-
Name (Acronym)Radar and Remote Sensing for Environment (RRSE)
-
Date07 April - 18 April 2025
(2 weeks, 30 hours/week) -
Teacher
-
Contact E-mail2024-2025.LM.RRSE.UniTN.TRENTO.IT@eledia.org
-
ECTS6
-
Syllabus
-
Institution
-
Study Program
-
Degree
-
LanguageEnglish
-
Tracks
ABSTRACT
The course is aimed to introduce the students to the basics of radar and remote sensing for environment, also providing insights on the latest advances as well as envisaged future evolutions. The course is divided into three parts. The first part presents the principles and the fundamentals of radar technology for remote sensing. In the second part, modern radar systems for remote sensing of environment are presented. The third part focuses on specific applications of remote sensing for environmental monitoring. The course is organized according to a learning-by-doing modality in which several numerical exercises, exploiting SW programs, will complete the theoretical lessons.
COURSE FORMAT
The Course is taught in 🇬🇧️ ENGLISH and offered
- On-site
- On-line (synchronous and asynchronous)
with video recordings, hand-outs, etc. of the lectures available off-line (*).
COURSE CONTENT
Part 1: RADAR PRINCIPLES
- Radar principles and objectives: passive/active radar; frequency spectrum; radar for detection, tracking, and imaging
- Radar basics: radar equation; radar cross section (RCS) and clutter; pulse repetition frequency (PRF); resolution capabilities in range and the non-ambiguous range; Doppler effect; range and velocity ambiguities
- Radar systems: monostatic, bistatic, and MIMO Radar
Part 2: RADAR AND REMOTE SENSING TECHNOLOGIES
- Continuous waves (CW), frequency-modulated continuous-wave (FM-CW), and pulsed radar: principles, general architectures, and main applications
- Synthetic Aperture Radar (SAR): SAR fundamentals; SAR acquisition geometries: conventional stripmap mode and spotlight mode; concepts of inverse SAR (ISAR) imaging; from image quality parameters to SAR specifications of HW and SW implementations
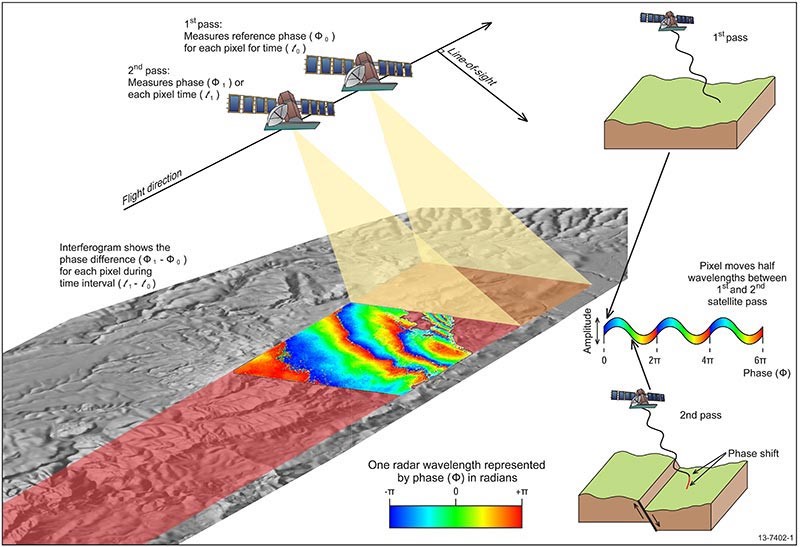
Part 3: REMOTE SENSING FOR ENVIRONMENTAL MONITORING
- Basic criteria for radar instruments selection
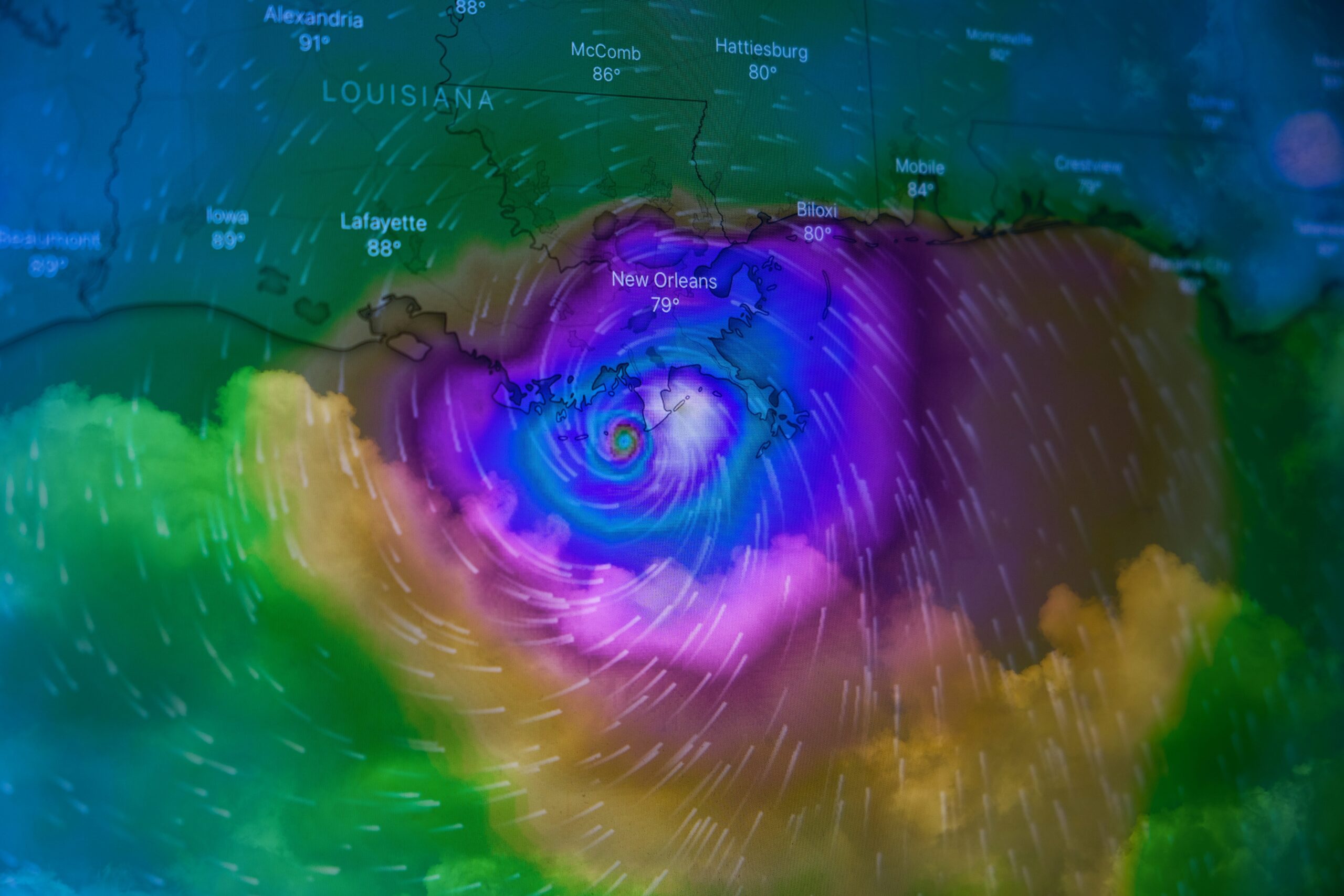
- Focus on weather radar: guidelines on how to collect, interpret and analyze environmental data according to World Meteorological Organization (WMO) standards and recommendations
- Read and analyze base reflectivity images, base velocity images, wind maps, and precipitation images
TEACHING ACTIVITIES
- Theoretical Lessons
- e-Xam Self Assessment (each teaching class or periodically)
- MATLAB Hands-On
- e-Xam Final Assessment
FURTHER READINGS
- M. I. Skolnik, “Introduction to Radar Systems”, McGraw-Hill, 2001.
- M. I. Skolnik, “Radar Handbook”, McGraw-Hill, 2008.
- G. Franceschetti and R. Lanari, “Synthetic Aperture Radar Processing”, CRC Press, 1999.
- H. Meikle, Modern Radar Systems. Artech House, 2008.
- W. L. Melvin and J. A. Scheer, Principles of Modern Radar: Advanced Techniques. SciTech, 2013.
- W. L. Melvin and J. A. Scheer, Principles of Modern Radar: Radar Applications. SciTech, 2014.
For further references please contact the Teacher(s).
(*) Each registered participant acknowledges that the material distributed in the frame of the course, available for the duration of one academic year, is protected by copyright and delivered for educational purposes and personal use only. The participant agrees and undertakes not to forward, publish, disclose, distribute, disseminate - in any form or manner - such a material without written consent of the author(s) of the material. Unless otherwise explicitly allowed by the speaker in written form, no recordings of the online lectures can be made.
